
Conventional KHIs include polymers 17, 18, antifreeze proteins 19, 20, ionic liquids 21 and quaternary ammonium zwitterions 22. KHIs delay nucleation and/or retard growth of hydrates at low dose (less than 1 wt%). However, due to economic and environmental concerns, kinetic hydrate inhibitors (KHIs) are currently receiving a great deal of attention as alternatives 15, 16. Traditionally, thermodynamic hydrate inhibitors (THIs) such as alcohols have been used to shift the formation conditions to lower temperature and higher pressure regions 10. One promising technology to overcome this problem involves the injection of hydrate inhibitors into the pipelines. Flow assurance for natural gas transportation and CO 2 sequestration becomes one of the most challenging area in the world energy industry 14. Safety and environmental issues derived from such accidents are clearly of major concern throughout the world. This results in significant financial losses for gas and oil companies due to the necessary pipeline shutdown and recovery, in addition to the potential for huge explosions such as those that were responsible for the Piper Alpha oil rig disaster (1988) and the Gulf of Mexico oil spill (2010). One important consideration is that gas and oil transportation lines often provide favorable temperature and pressure conditions for gas hydrate formation, resulting in a build-up of hydrates and subsequent pipeline blockage 13. The foundation of the energy industry now moves towards gas.Īccordingly, the pipeline transportation technology is becoming increasingly significant due to a vast amount of the gas fuel production and CO 2 emission from the gas fuel combustion. In a similar context, gas hydrates, crystalline water-based solids in which gas molecules are enclathrated in a framework linked by hydrogen bonded water molecules 10, as promising energy resources are within reach 11, 12. It has been estimated that shale gas could supply decades of use for worldwide energy consumption 9. Instead, shale gas reached recent headlines as it became commercially available from technological advances in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing. However, there is still no solution that adequately meets the rapidly increasing energy demands of the world.

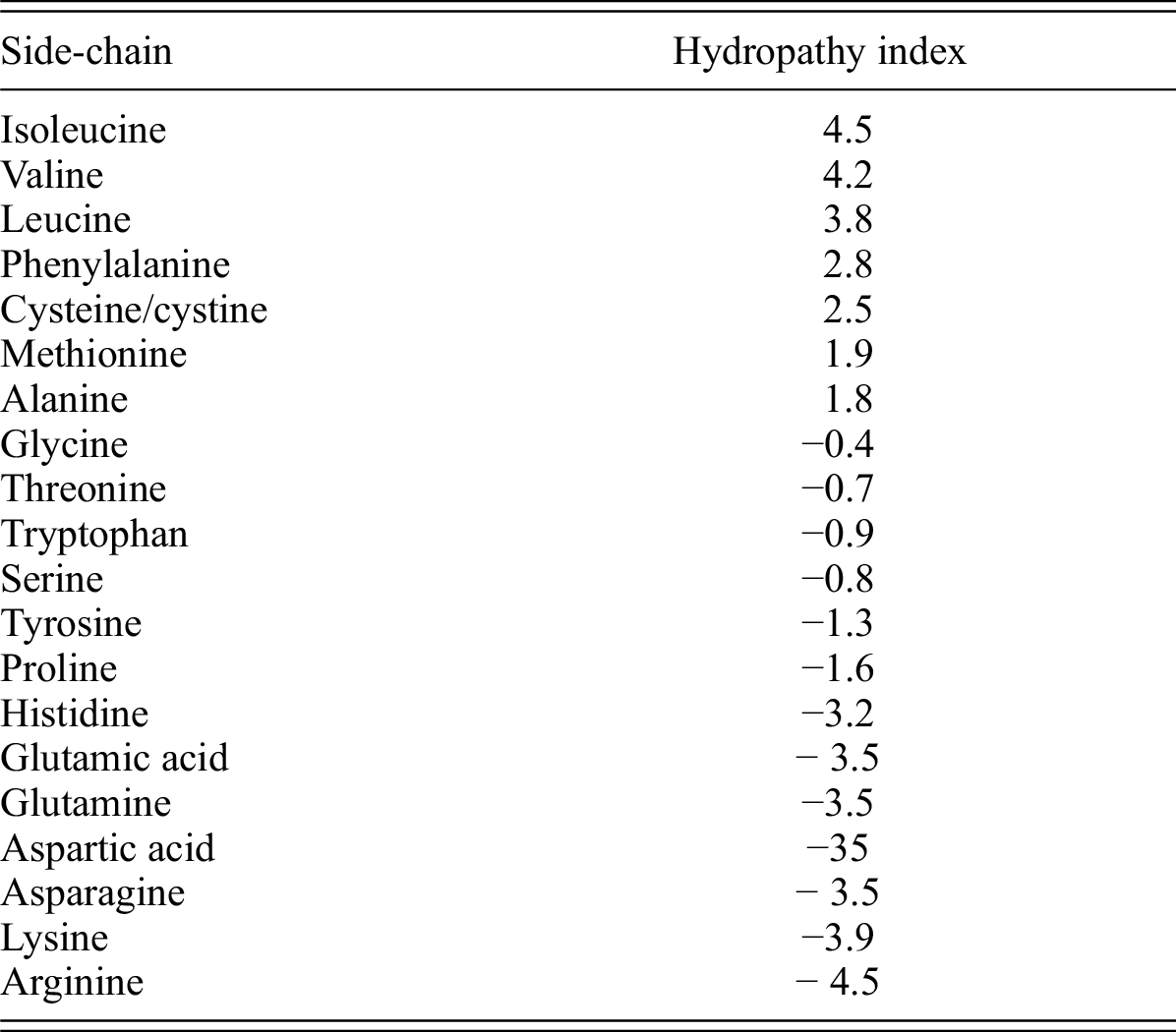
This suggestion of a new class of KHIs will aid development of KHIs with enhanced biodegradability and the present findings will accelerate the improved control of hydrate formation for natural gas exploitation and the utilization of hydrates as next-generation gas capture media.Īs the energy crisis and increasing levels of environmental pollution are being addressed as the major challenges affecting the modern world, mankind has been steadily seeking new alternative clean energy resources 1, including hydrogen 2, 3, 4, solar 5, geothermal 6, wind 7 and biomass energies 8. It was found that perturbation of the water structure around KHIs plays a critical role in hydrate inhibition. Amino acids with lower hydrophobicity were found to be better KHIs to delay nucleation and retard growth, working by disrupting the water hydrogen bond network, while those with higher hydrophobicity strengthened the local water structure. Here, we examined natural hydrophobic amino acids as novel kinetic hydrate inhibitors (KHIs) and investigated hydrate inhibition phenomena by using them as a model system. However, the principle of hydrate inhibition is still poorly understood. As the foundation of energy industry moves towards gas, flow assurance technology preventing pipelines from hydrate blockages becomes increasingly significant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
